Enquiry List () (0)
- 23 Jun 2022

Refining Safety Measures of the Pulp and Paper Industry to Mitigate Common Dangers

Asia is home to the largest producers of pulp and paper in the world. China singlehandedly produces over 99 million tons worth of material each year, followed by Japan which produces an additional 26 million tons. A combination of hundreds of different chemicals will be used throughout the laborious process by different manufacturers worldwide. With this many solutions involved in the process it is essential that workers are aware of the hazards they work with and have access to safety showers and eye/face washes in the event of a chemical spill.
 After the initial process of selecting and de-barking the trees, raw materials are broken down into wood chips before being cooked and refined. Peroxides are used in delignification, the process of extracting the useful fibres from the lignin, which is responsible for discolouring the pulp. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, often used in this process, can cause severe reactions when contacting the skin and eyes. Minimal contact can cause severe blisters and ulceration of the skin or cornea, even resulting in permanent blindness.
After the initial process of selecting and de-barking the trees, raw materials are broken down into wood chips before being cooked and refined. Peroxides are used in delignification, the process of extracting the useful fibres from the lignin, which is responsible for discolouring the pulp. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, often used in this process, can cause severe reactions when contacting the skin and eyes. Minimal contact can cause severe blisters and ulceration of the skin or cornea, even resulting in permanent blindness.
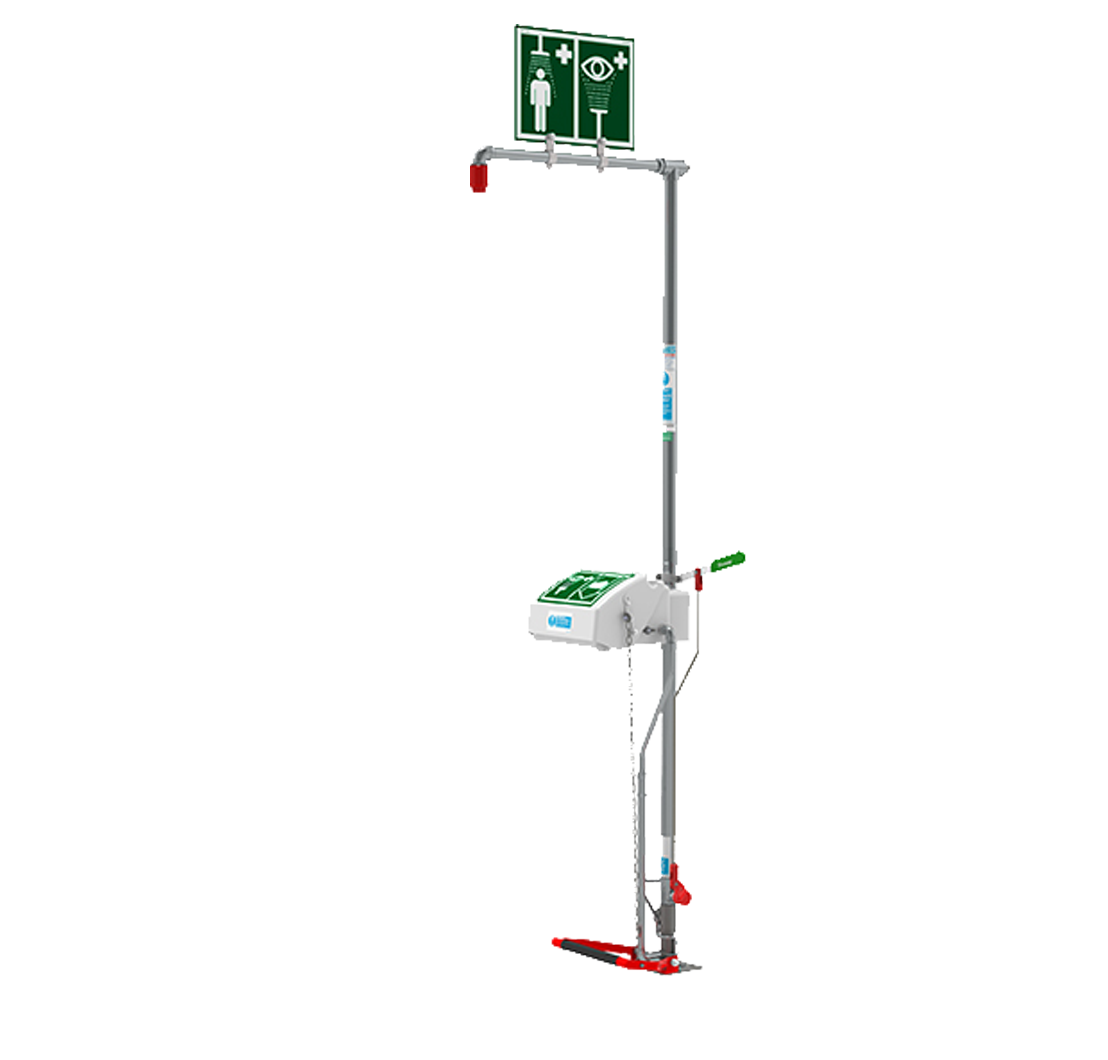
To prevent serious injury, a casualty should immediately flush the site with tepid water. The Hughes self-draining safety shower with ABS closed bowl eye wash can be connected to a constant water supply to ensure a thorough decontamination of the eyes and skin for at least 15 minutes, as outlined by EN15154 requirements. The eye wash features an ABS protective lid which can be pulled down for automatic activation in the event of an emergency and provides added protection from debris and contaminants. An optional treadle can be installed for hands-free activation while the self-draining valve prevents from hot water build up in the extreme heat of the environment.
Once the lignin has been extracted, the pulp can then be washed and bleached at which point solutions such as chlorine dioxide are introduced to lighten the colour of the pulp. Chlorine dioxide can dehydrate the skin, increasing trans epidermal water loss and exacerbating pre-existing skin conditions. In areas with poor ventilation the chemical can also cause burns or damage the eyes, causing the casualty to see halos around lights. Another chemical used to improve the optical quality of paper at this stage is quicklime. Quicklime can adversely affect eyes and skin and it is therefore recommended that if contact is made with the eyes, the casualty should flush their eyes thoroughly with water for 15 continuous minutes.
After the pulp has been refined into sheets, excess water is pressed out to decrease the fragility of the product. From start to finish, water plays an essential part in the production of pulp and paper, after which, as much water as possible is sent for treatment and recycling.
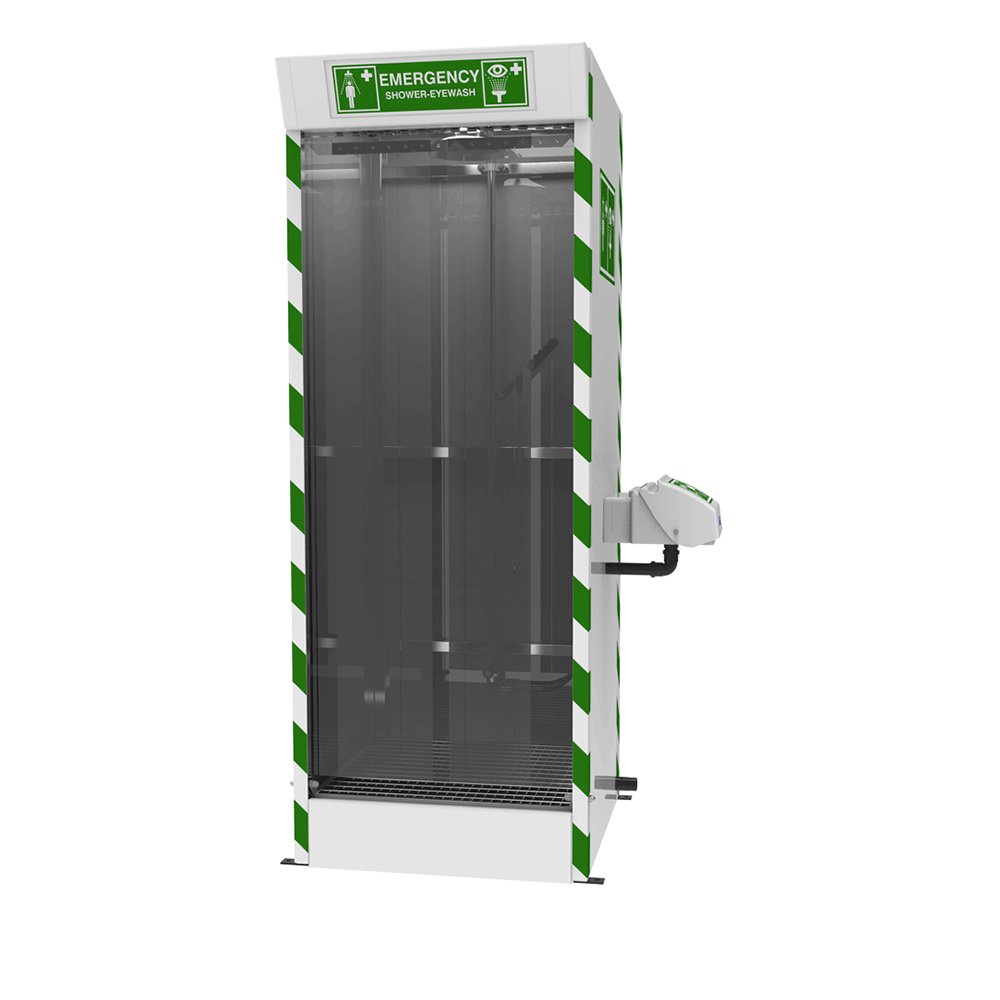
Hughes range of indoor safety showers can provide immediate relief to a casualty in the event of a chemical spill. Our range of combination showers can ensure that, in the event of a spill, the eyes and skin can be flushed simultaneously at a flow rate designed to meet international standards. To help prevent splashes from contaminated water, the Hughes STD-SD-32K/45G cubicle shower is designed to protect the surrounding area and provide a designated decontamination area. A GRP sump is included to contain and dispose of the contaminated water easily when connected to suitable drainage.
Hughes Safety Showers specialise in safety equipment that is designed to meet ANSI and EN15154 requirements in the eventuality of workplace chemical accidents. To discuss your requirements or obtain a quote from one of our experts, fill out our contact form and a member of our team will be in touch.
References:
Top 10 Pulp & Paper Producing Countries In World (WorldPaperMill.com)
Chemicals Used in Paper Making Process (PaperOnWeb.com)
Chlorine Dioxide Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet (NJ.gov)
Hydrogen Peroxide in Paper Industry (Belinka-Perkemija.com)